Earthquake Risk and Risk Development in the Megacity Istanbul
Project duration 2004 - 2007. The final results of the projects have been presented at AKOM Istanbul on October, 22nd 2008 (Agenda Link). The results are also available in the final project documentation: final report
Introduction
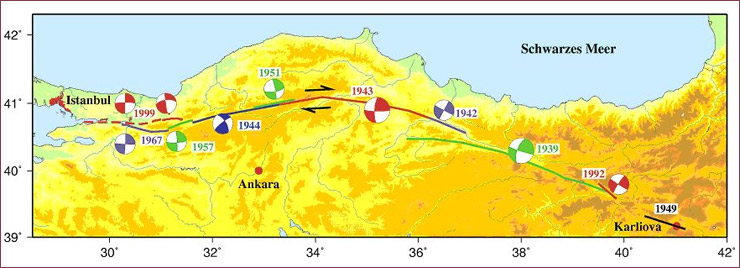
The megacity Istanbul is ranked, according to the GESI 2001 study made by Geohazard International, second in the list of investigated megacities concerning expected casualties in case of an earthquake. Since then, its population has grown by approximately 250.000 inhabitants per year. Therefore, the earthquake risk for Istanbul is changing due to population growth, the resulting building activity, but also due to a change in earthquake hazard caused by stress accumulation and stress transfer from previous events (see Figure 1).
Figure 1 Apparent westward migration of earthquakes along NAFZ (Grosser, GFZ, 2001).
Aims
CEDIM aims at developing methods for monitoring earthquake hazard, fragility, and vulnerability. These methods should allow for near real-time updating of relevant parameters in order to cope with the development of the city. Following the risk chain the results and methods developed in the four sub-projects Numerical stress field modelling, Microzonation, Fragility & Vulnerability, and Indirect Losses will be merged and made available for catastrophe management and urban planning.
Related projects and partners
Related research is financed in the framework of the I-EOS (Integrated Earth Observation System) PhD program of the Helmholtz Gemeinschaft . The GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam supports the project with further research activities in the region.
Zu den Teilprojekte:
» Fragility and Vulnerability
» Local Site Effects
» Socio-Economic Impacts
» Stress Field Modelling in the Marmara region