Short Reports
2025
|
Heavy rain Central Europe (September 2025) |
|
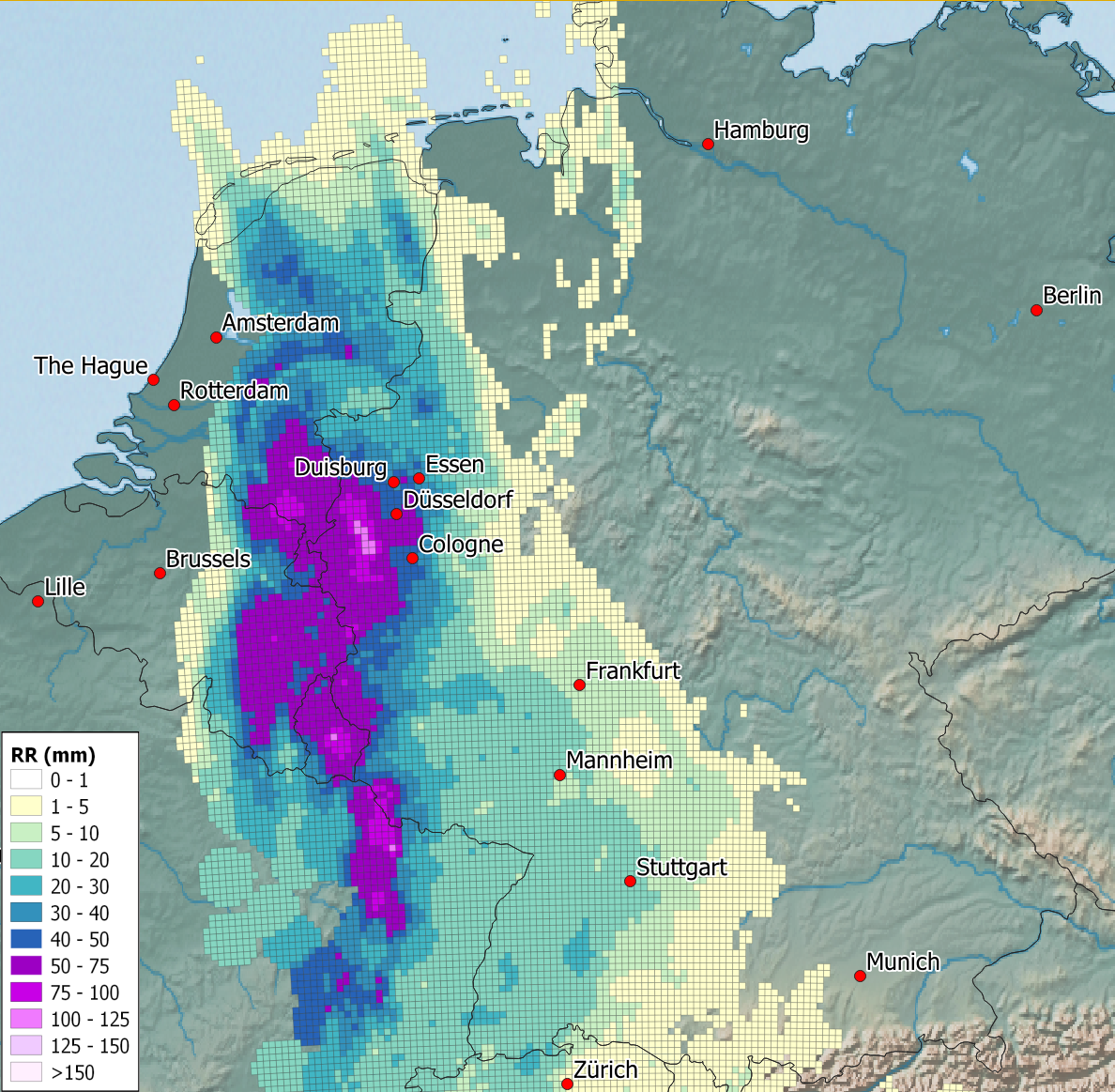 |
Almost exactly one year after the extreme rainfall in eastern Central Europe, which caused devastating floods, another heavy rainfall event occurred in Central Europe. This was accompanied by the low-pressure system 'Walter II', which moved from southern France to Germany, causing heavy rainfall on 8 and 9 September 2025. Precipitation amounts of more than 100 mm were recorded across a wide area within 12 to 18 hours. In Germany, the precipitation was concentrated in the western parts of Saarland, Rhineland-Palatinate and North Rhine-Westphalia, as well as in neighbouring areas of Luxembourg, Belgium and Lorraine. At the beginning of the event, the rain was particularly heavy and convective, accompanied by thunderstorms. According to KOSTRA 2020, the return periods of precipitation exceeded 100 years in parts of Saarland and western North Rhine-Westphalia. Where thunderstorms were recorded, the annual frequency of continuous precipitation for one hour was greater than 100 years. However, in most cases, the return period of more than 100 years refers to continuous precipitation levels of between 6 and 18 hours. Despite the enormous amounts of rain in some areas, the overall impact was not particularly dramatic. Only in Luxembourg did the Alsette river reach a level corresponding to a flood that occurs every 5 to 10 years; elsewhere, water levels remained lower. In areas affected by heavy rainfall, there was some overflowing and minor flooding. Underpasses and some basements flooded, and meadows, fields and roads flooded in places. A highway had to be closed.
to the report (12 September 2025) |
2024
|
Heavy rain Middle East (April 2024) |
|
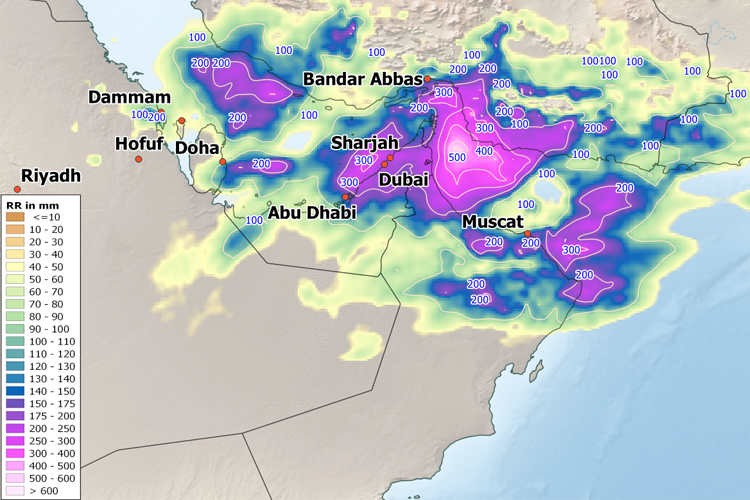 |
In mid-April 2024, a trough slowly moving eastward across the Arabian Peninsula triggered intense rainfall. In the United Arab Emirates, northern Oman, and southern Iran along the Persian Gulf coast, several 100 mm of rain fell in some areas. The United Arab Emirates set a new historical rainfall record on April 16, 2024, when 254.8 mm of rain fell in less than 24 hours at Khatm al-Shakla in the al-Ain region; measurements there began in 1949. Major flooding occurred, with many streets in Dubai submerged and major roads affected. Many flights were canceled or delayed at Dubai airport. In Oman, the floods caused at least 20 deaths.
to the report (25 April 2024) |
2023
|
Heavy rain Greece & Libya (Sept. 2023) |
|
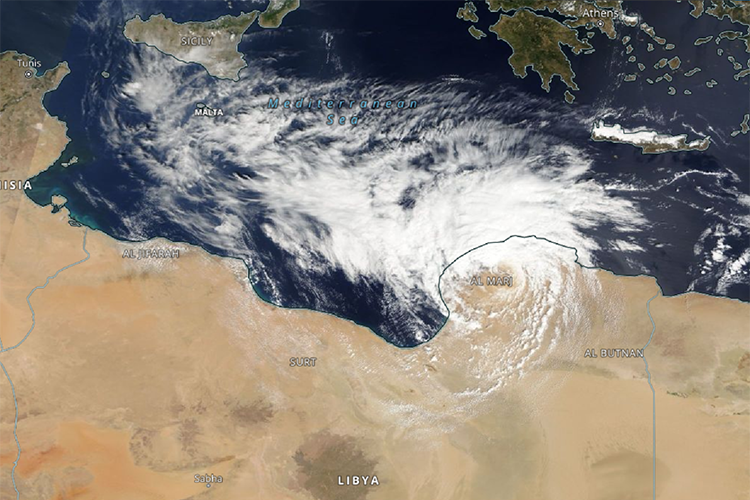 |
From the end of August to mid-September 2023, the Mediterranean region was characterised by intense low-pressure activity. Low pressure "Erwin" already led to extreme precipitation, landslides, and flooding in northern Italy from 28 to 30 August. At the beginning of September 2023, enormous amounts of precipitation occurred in the western Mediterranean region in north-eastern Spain, while low pressure "Daniel" began to form further east. "Daniel" formed on the south-eastern flank of a huge blocking area of high pressure over central Europe ("Omega situation") and caused storms, heavy rainfall, and flooding first in Greece and a few days later as a so-called Medicane in Libya. The torrential rain led to the collapse of two dams, whose masses of water rolled through the Libyan port city of Derna, killing thousands. Entire districts were washed away and more than 3000 buildings were completely destroyed.
to the report (20 October 2023) |
2022
|
Paktika earthquake in Afghanistan (June 2022) |
|
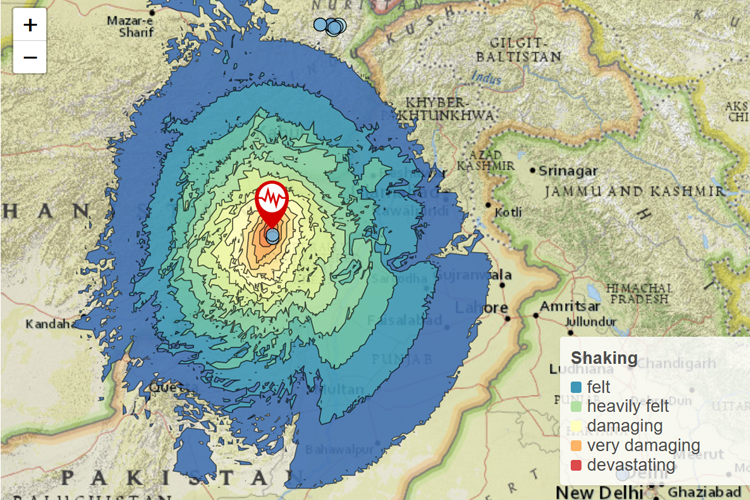 |
An earthquake measuring magnitude 6.2 occurred on the Afghanistan-Pakistan border at 01:24 local time on June 22, 2022 (at 20:54 UTC on June 21, 2022). Mainly Paktika and Khost provinces and parts of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in Pakistan were affected. At least 1000 people were killed, over 3500 people were injured, and at least 25,000 were left homeless.
to the report (5 July 2022) |
|
Torrential Rain & Flooding in South Africa (April 2022) |
|
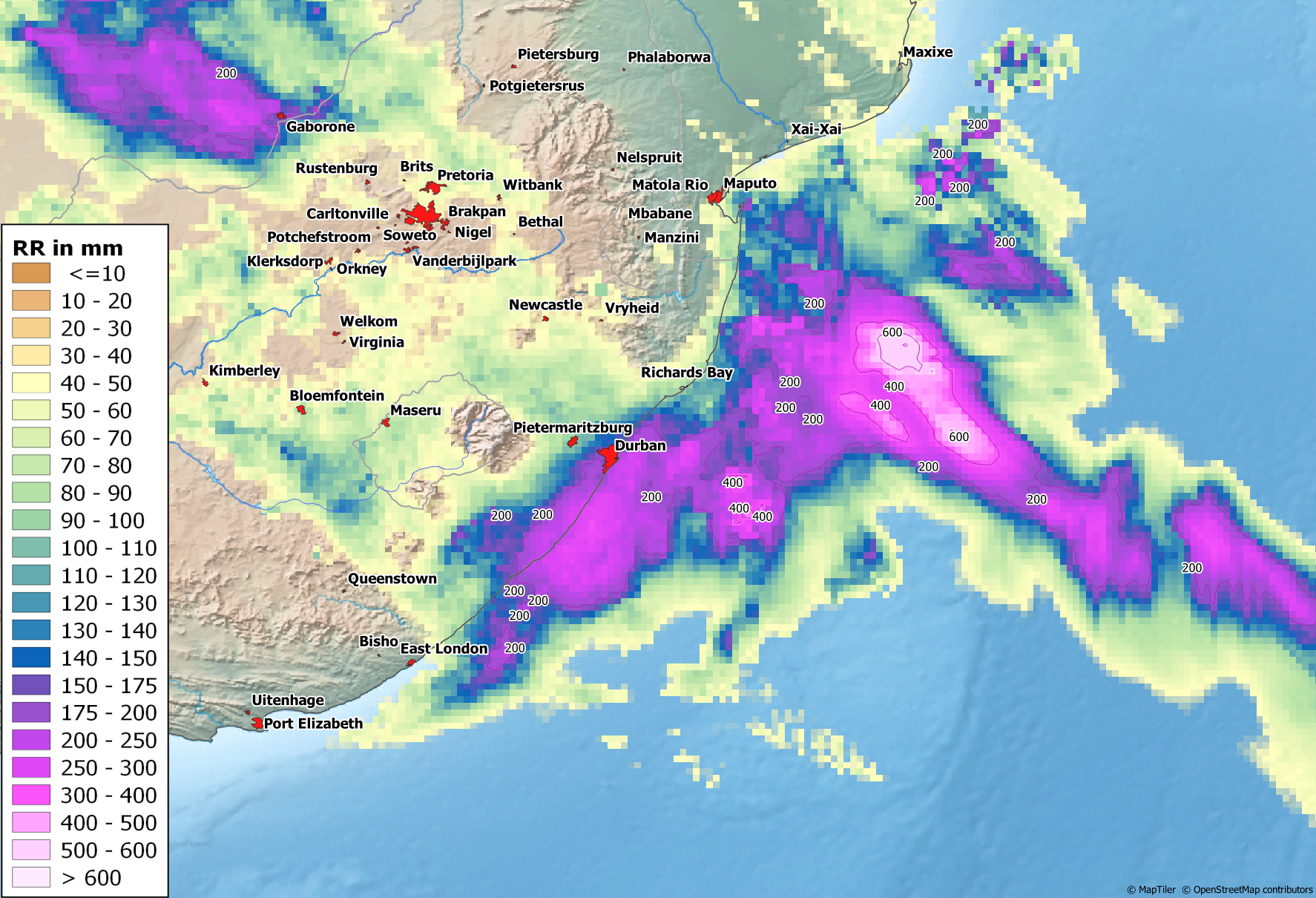 |
Around three months ago (Jan. 2022), parts of South Africa were already the place of repeated and in some cases extreme rainfall, which led to major flooding and claimed several lives. The Eastern Cape and KwaZulu-Natal provinces in particular suffered major damage. In April 2022, areas near the coast of KwaZulu-Natal province were again hit by heavy rainfall. Within two days, some stations recorded rainfall totals of around 450 mm, and in some places around 300 mm within 24 hours. In view of such rainfall, the numerous landslides, destroyed bridges and roads, and thousands of damaged or demolished buildings come as no surprise. At least 395 people lost their lives. Partly responsible for the devastating rains was the subtropical depression 'Issa', which - quite surprisingly - had formed immediately off the coast of KwaZulu-Natal. With nearly 400 fatalities, Issa and a neighboring high trough to the west became the deadliest storm event in South Africa's history.
to the report (17 April 2022) |
|
Winter storm series, February 2022 (NW & Central Europe) |
|
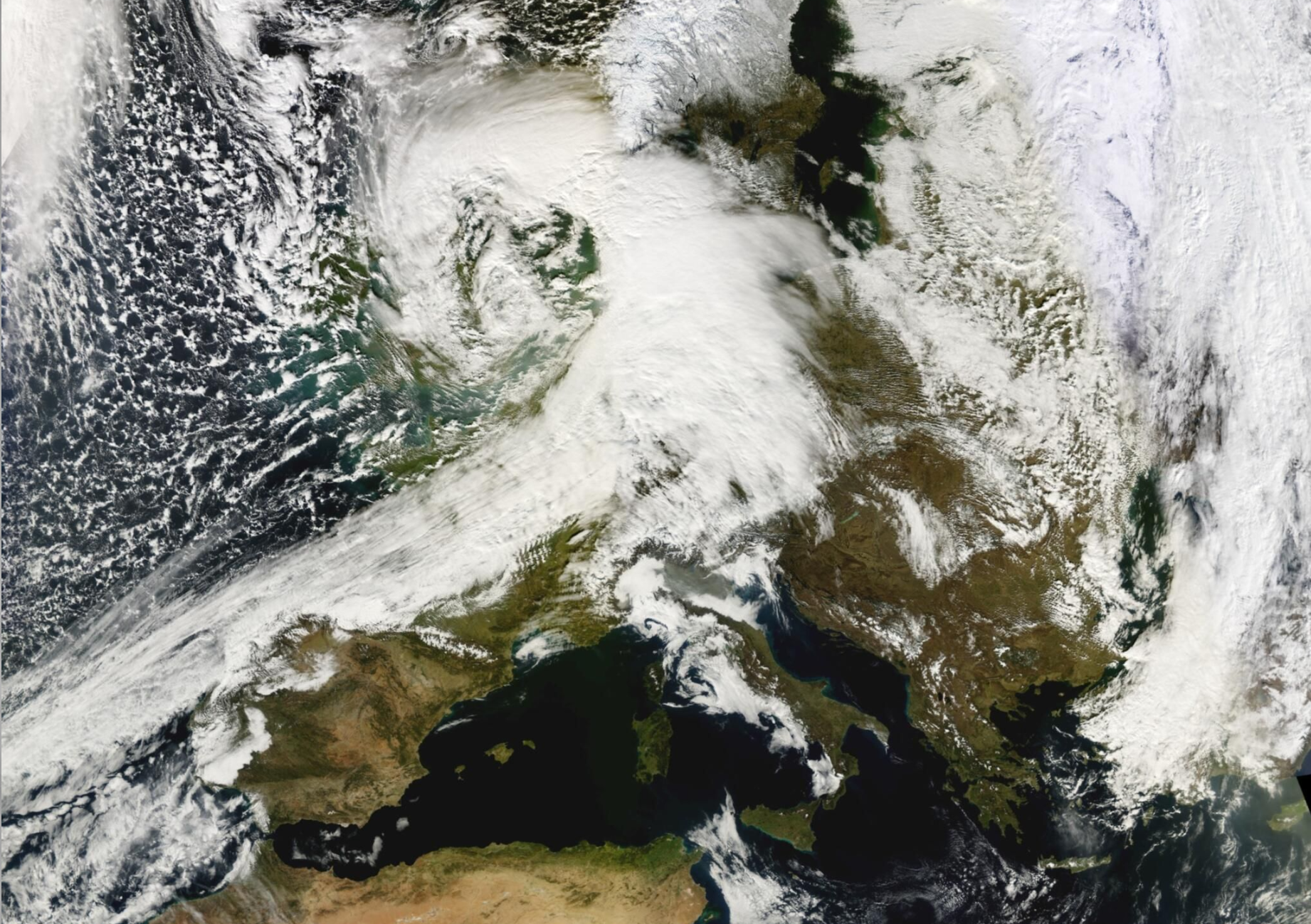 |
Over a period of about a week, a series of powerful low-pressure systems swept across northwestern Europe and northern Central Europe. The wind fields of the very intense low pressure systems particularly affected the south of Ireland and England, northern Belgium, the Netherlands, the northern half of Germany, and the southwestern Baltic Sea region. Gale-force winds were recorded in many places, and even inland the wind reached speeds of more than 118 kph in places. The Needles station on the Isle of Wight possibly set a new wind speed record for England with as much as 196 kph. These extraordinary wind speeds were most likely caused by a so-called sting jet. New peak wind speeds for the month of February were also recorded at some stations in Germany. Hundreds of thousands of people were affected by power outages, and there were also considerable restrictions, particularly on rail services, which were completely shut down in some regions. Hamburg recorded a very severe storm surge for the first time since 2013, with water levels exceeding 3.5 meters above mean high tide. The hurricane-force low pressure systems claimed several lives and caused major property damage, which initial estimates put at more than 1 billion euros for Germany alone.
to the report (4 March 2022) |
|
Heavy rain (South Africa)
|
|
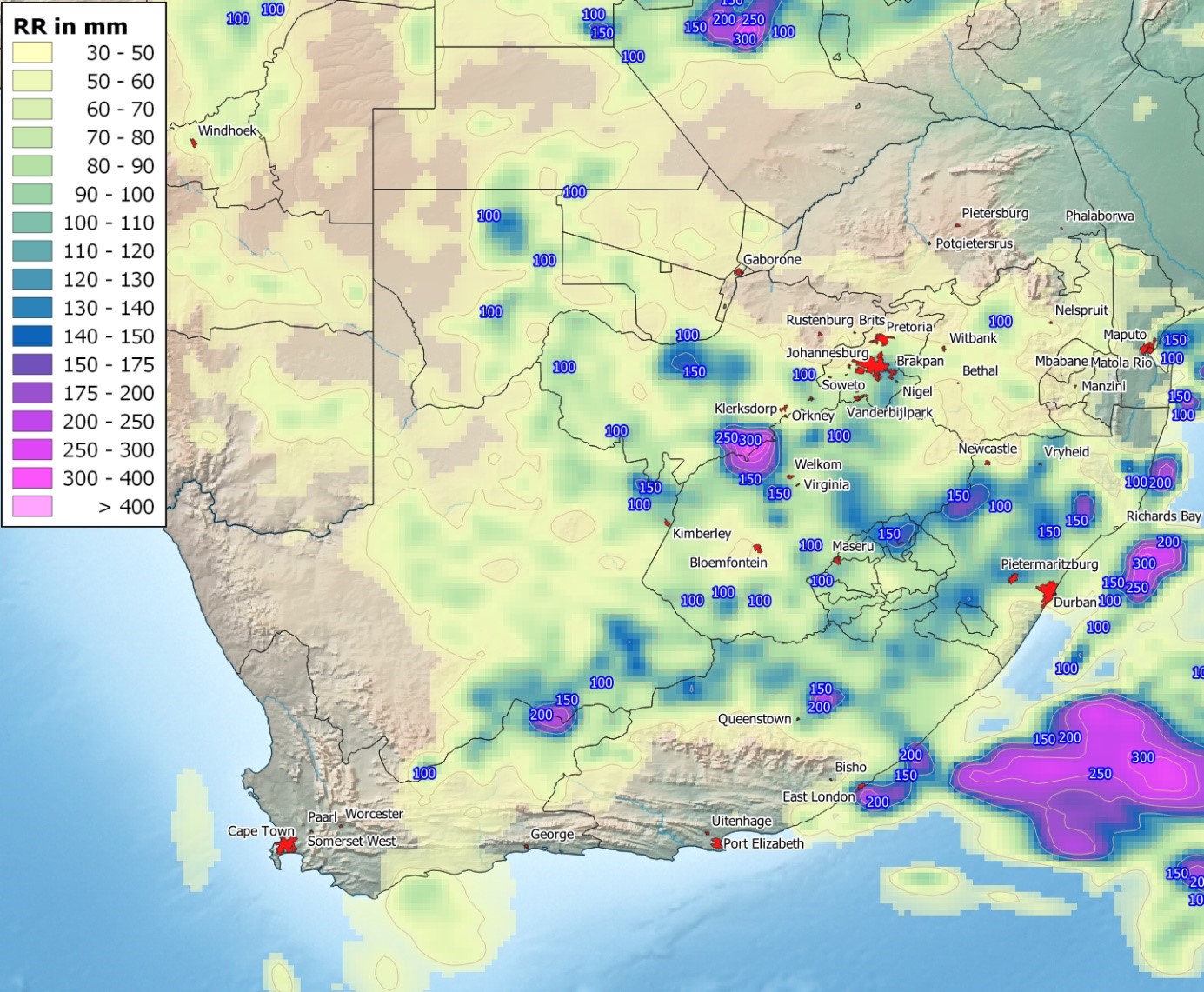 |
In South Africa, areas in the very south of the country received little or no precipitation in summer - Cape Town, for example, has a Mediterranean climate with predominantly winter rainfall - while other parts of the country experienced extremely heavy rainfall. In January 2022, however, areas of convective precipitation repeatedly brought in some cases extreme amounts and intensities of rain, resulting in major flooding in some places. The Eastern Cape and Kwazulu Natal provinces in particular suffered major damage and a number of fatalities.
to the report (20 January 2022) |
|
Volcano & Tsunami Hunga Tonga (Pacific)
|
|
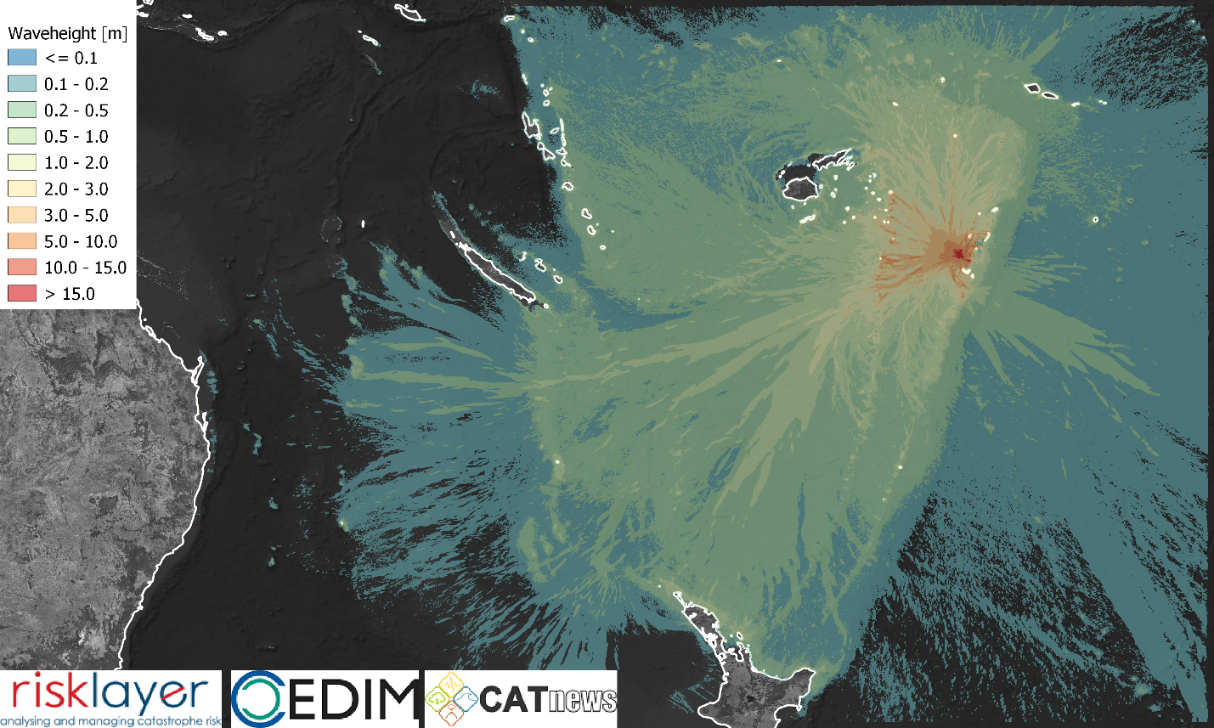 |
The volcanic eruption in the South Pacific (Tonga Islands) in mid-January 2022 was the world's strongest since the eruption of Pinatubo. Hunga Tonga is a large undersea volcano about 70 km North-West from Tongatapu (Southwest Pacific). The volcano is formed by 2 small islands, Hunga Tonga and Hunga Ha'apai, have been connected by recent eruptions in 1988, 2009 and 2014-2015. The eruption sequence started on Dec. 20th, 2021 with a single eruption. It was followed by a larger event on Jan. 14th and the main eruption starting on Jan. 15th around 17:15 local time (04:15 UTC). All eruptions were associated with a load sonic boom. The explosion of the main eruption was heard over thousands of kilometers. The main eruption triggered a major mass movement, which is the anticipated source for the tsunami afterwards. The tsunami was observed on Tongatapu within 15 min and disrupted energy supplies. The tsunami was observed all around the Pacifc and Coral & Tasman sea with run-ups of up to 3 m. Severe local flooding occurred on Tonga (run-up of 2 to 5 m) and local minor to moderate inundation along the Coral Sea (< 0.5 – 3 m) and along the Pacific Ocean (0.5 – 1.5 m). Several islands of Tonga were partially inundated. The small, uninhabited islands of Nuku and Tau were completely eroded. Inundation on Tongatapu and Nomuka destroyed several buildings. Coral reefs and barrier islands played an important role in reducing the tsunami’s impact. The major damage is associated with the breakage of the undersea cable from Fiji to Tonga. The economic losses associated with such an outage will be large, given the costs and scarcity of satellite phones. A major problem at present is ash on the Tongatapu airstrip, meaning that relief planes are mostly unable to land to deliver aid. Additional costs associated with cleanup and ash removal will also be incurred in agriculture, as well as potential infrastructure problems due to contamination of the water supply.
to the report (18 January 2022) |
2021
|
Heavy Rain (USA, California)
|
|
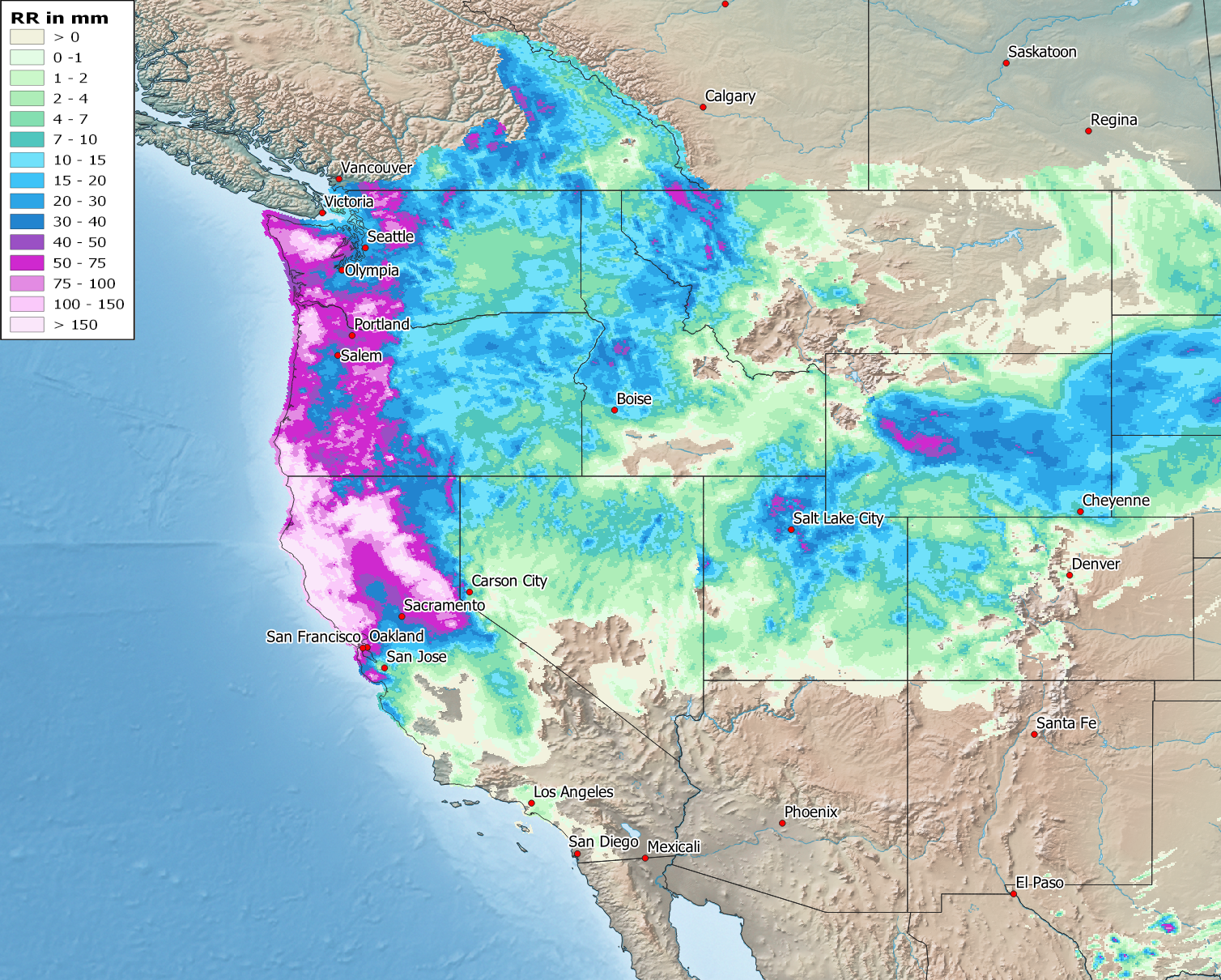 |
At the beginning of the third decade of the month, the northeastern Pacific experienced unusually active low-pressure activity for October. Several strong low-pressure systems reached far south with their frontal systems and caused heavy rainfall, especially in the central and northern parts of California; at higher altitudes, there was abundant snow and gale-force winds in many places. Daily precipitation values reached more than 200 mm, with the total precipitation event amounting to 380 mm. The long-term average monthly precipitation in Central and Southern California is typically 10 to 40 mm. Thus, within one week, precipitation amounts in some areas reached more than 1000 % (ten times) of the amount usually occurring during this period. Even San Francisco, where usually only 27 mm accumulate in a whole month of October, recorded rainfall amounts around 100 mm. Floods and landslides occurred, and there were interruptions in the power supply.
to the report (26 October 2021) |
|
Storm Hendrik/Ignatz (Gemany)
|
|
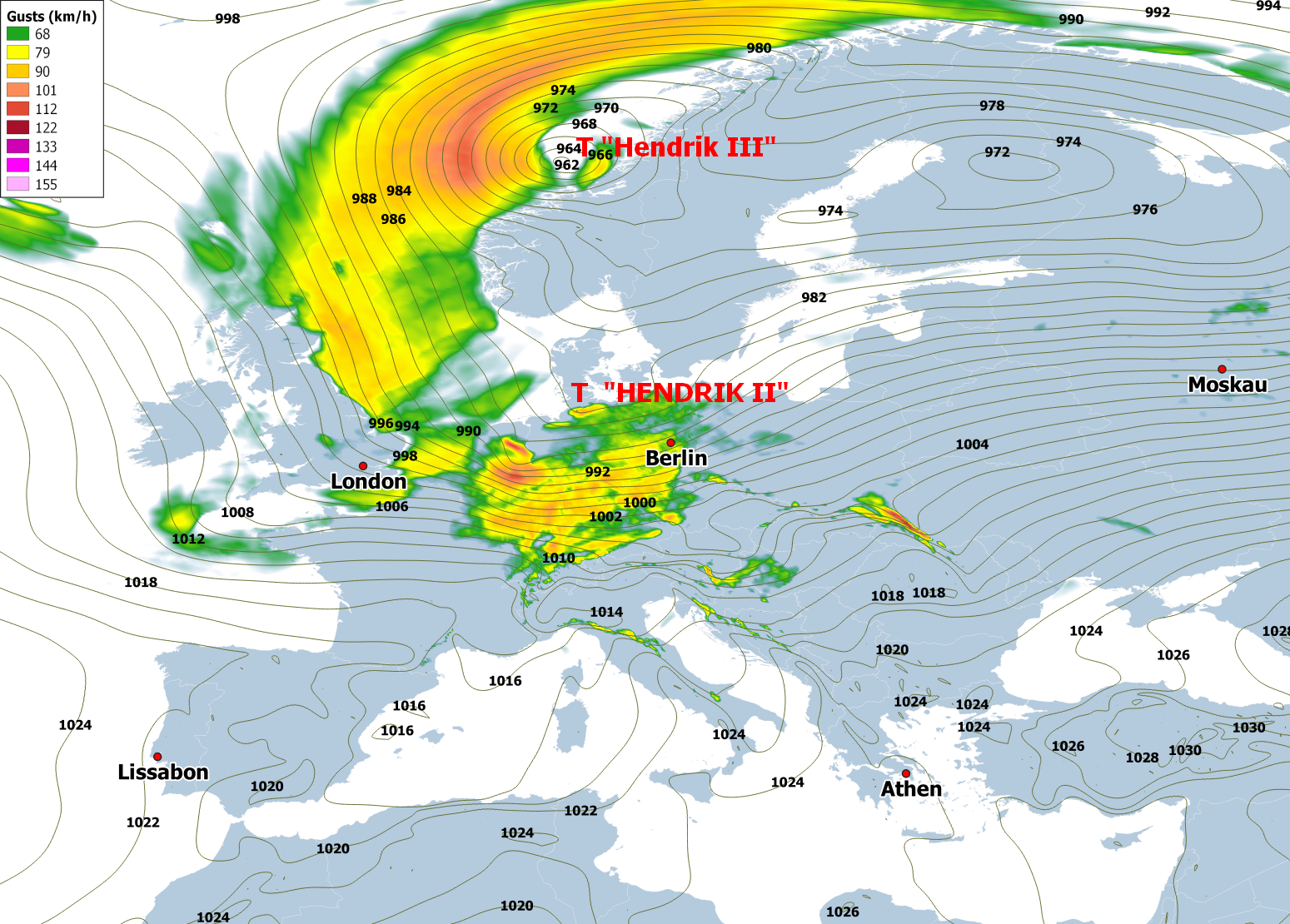 |
The first storm of the 2021/2022 autumn and winter season crossed Central Europe with its storm field on October 21 and particularly affected the central parts of Germany. Even in the lowlands, isolated gale-force winds occurred, such as in Dresden-Klotzsche with 119 km/h; the strongest gust was recorded by the Feldberg station in the Black Forest with 166 km/h. Numerous trees fell and damaged some overhead lines, and power was lost for several tens of thousands of residents. There were considerable restrictions on road and rail traffic. Although the storm can be described as unusual and severe for October - several stations recorded new record wind speeds for the month - it was not one of the strongest autumn and winter storms of the past 40 years.
to the report (25 October 2021) |
|
Snowfall / Cold spell February 2021 (Germany)
|
|
 |
After an unusually strong dust transport from the Sahara, an extremely cold weather period began in the first decade of February 2021, at least in parts of Germany. It lasted for about 10 days in the center and east of the country, but towards the south and west, the cold weather decreased significantly in intensity and duration. Record snowfalls, which occurred simultaneously with strong easterly winds, left a thick blanket of snow from North Rhine-Westphalia to Saxony, which accumulated to a height of more than half a meter in some areas, even in the lowlands. In continental cold air under the influence of high pressure and above the freshly fallen snow, the thermometer often dropped below -20 °C, and in some places new records were set for the lowest temperature in February. Temperatures reached values as low as -26.7 °C in Thuringia. In the central parts of the state in particular, the snow and high snow drifts caused considerable obstructions on roads and railways, and in many places traffic came to a standstill or was suspended. Severe frost also caused icy conditions on some rivers and canals, and inland shipping was not only suspended on parts of the Mittelland Canal. Coastal ice also formed on the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Despite several new temperature and snow depth records, however, the cold weather period remains far behind the extreme events of past February months, such as the years 1929, 1947, 1956, 1963 or 1986.
to the report (23 March 2021) |
|
Heavy Rain & Flood January 2021 (Germany)
|
|
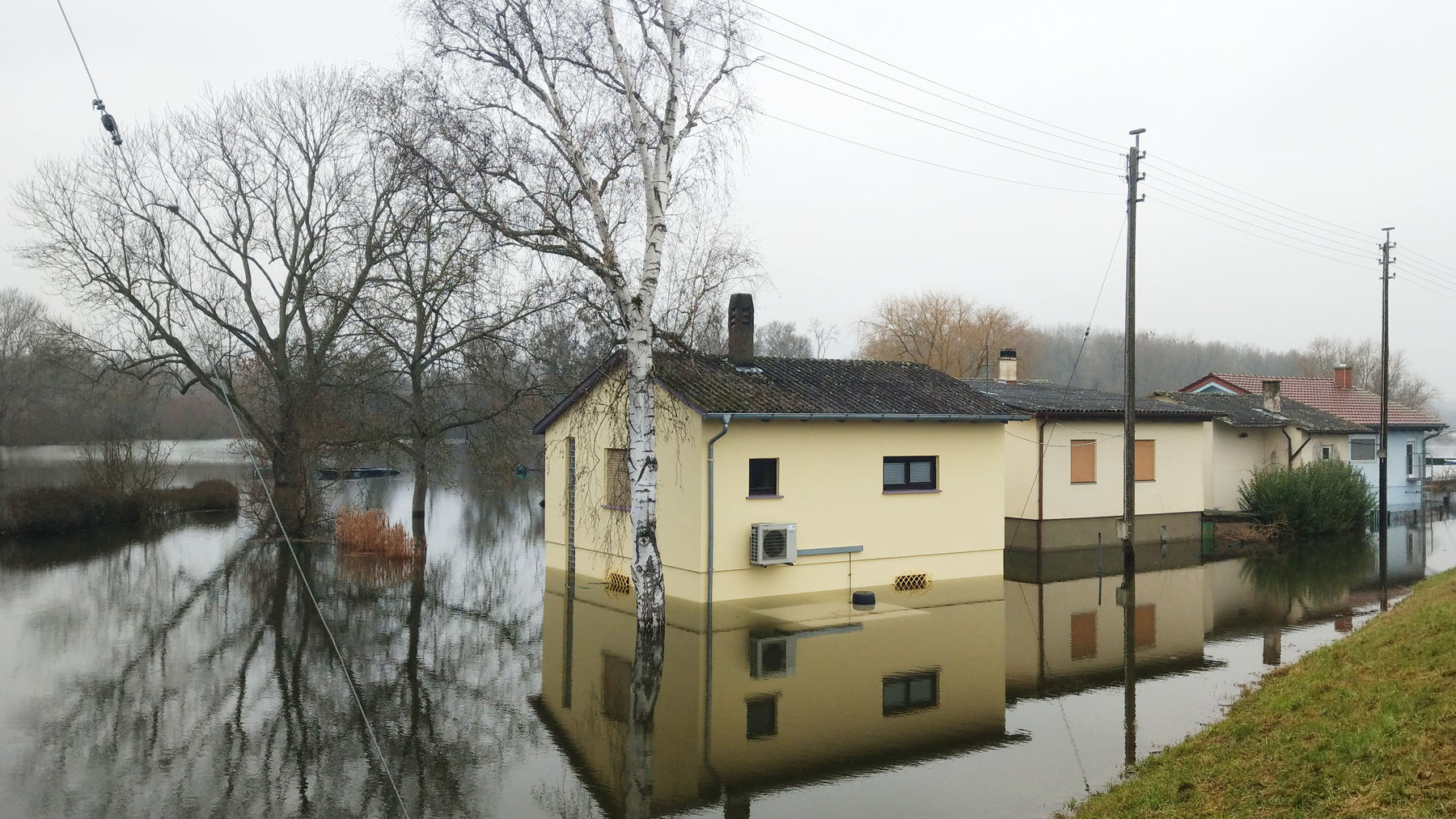 |
After a period of cold and wintry weather, which was accompanied by heavy snowfall in some areas, rainy and mild weather prevailed in southern Central Europe towards the end of January 2021. Embedded in a strong westerly flow, several low-pressure systems transported moist and very mild air masses. A heavy thaw set in at altitudes above 1,500 meters, which, together with intense rainfall, increased the levels of numerous rivers in central and southern Germany and northern Switzerland. Most rivers in Baden-Württemberg, in northern Bavaria, and in central and eastern Hesse registered floods with a return period of 2 to 10 years. Occasionally, however, water levels occurred that occur only once in 20 to 50 years. In central and eastern Hesse, new historic maximum water levels were even observed at individual gauges. The levels and discharges of the major rivers Rhine and Danube were not unaffected as well. At the gauge of the Rhine in Karlsruhe-Maxau, the water level reached its crest value of 851 cm in the night of January 31, 2021, which corresponds to a 5- to 10-year flood. Major flooding occurred mainly in the lower reaches of rivers draining westward and southward from the Black Forest (e.g. Gutach), in the northern vicinity of Lake Constance (e.g. Schussen), in northern Bavaria and in eastern Hesse (catchment areas of Fulda and Nidder). A protective wall of the Seemenbach could not withstand the water pressure and the water poured into the old town of Büdingen in Hesse.
to the report (1 February 2021) |
2020
|
Heavy rain/Storm February 2020 (Germany)
|
|
 |
More than two days of continuous rain, which occasionally added up to more than 200 mm, led to rapidly swelling streams and rivers, especially in southern Germany. Many of them led to flooding. Several rivers in Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland, Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria were flooded with a return period of between 2 and 10 years. However, there were no extreme floods on larger rivers. In some areas, streams and rivers overflowed or overflowed their banks and flooded adjacent properties, meadows and roads. Some road connections were disrupted, and the railway also ceased operation on the section between Perl and Trier, for example. Responsible for the heavy rain was the continuous influx of mild and very humid air masses. A strong westerly to south-westerly current caused an effective humidity replenishment to Central Europe, which was particularly noticeable in the low mountain ranges and near the Alps, where precipitation increased. The first three days of February 2020 not only brought local precipitation records, but also new temperature records, and at the end of the weather period new wind records for the month of February occurred sporadically.
to the report (4 February 2020) |
|
Drought & Fire 2019/2020 (Australia)
|
|
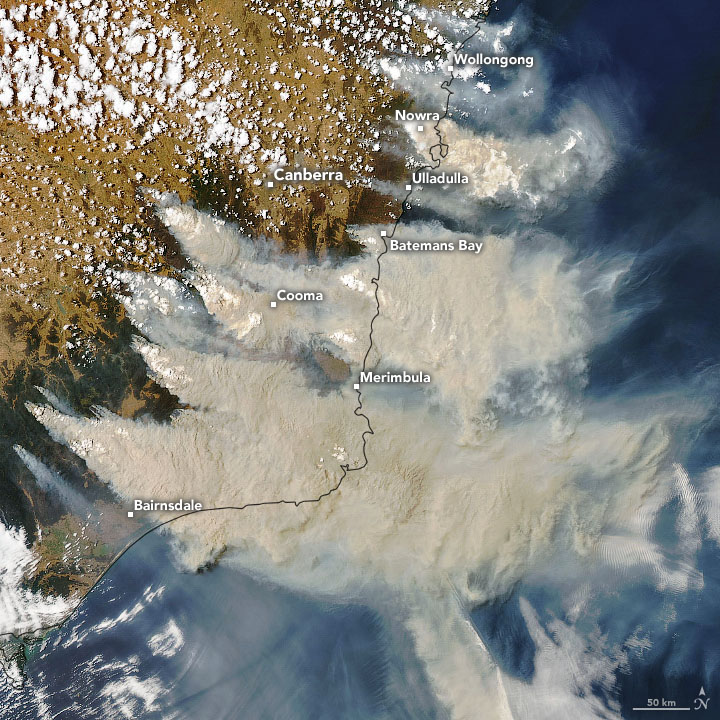 |
In 2019, the Australian continent experienced its warmest and driest year since records began in 1910. The nationwide mean temperature of the year was 21.8°C, 1.52°C above the long-term average of the reference period 1961-1990, resulting in exceptional heat waves in January and December. In addition, January, February, March, April, July, October and December were already among the 10 warmest months since records began. The associated fires and their clouds of smoke caused extreme air pollution and dangerous concentrations of pollutants, for example along the coast of New South Wales and also in the greater Sydney area.
to the report (24 January 2020) |
|
Earthquake in Turkey (Doganyol, 24 January 2020)
|
|
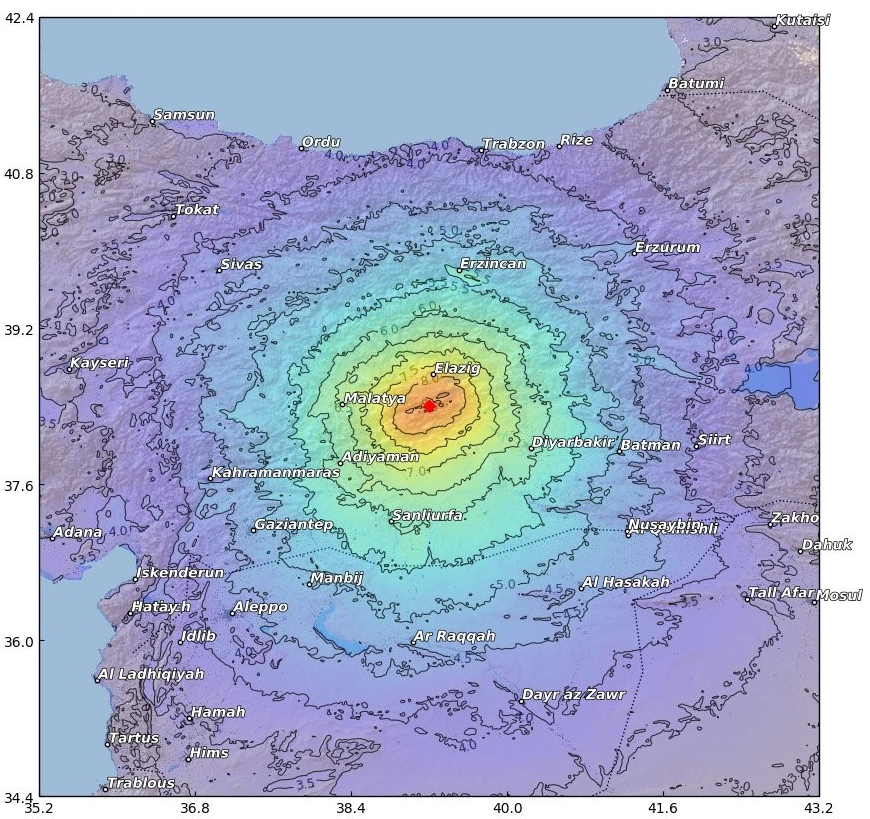 |
Intensities reached VIII on the MMI scale – very well built structures received slight damage. Older buildings suffered great damage. There was also limited liquefaction. The damage seen corresponds to VIII and perhaps very isolated VIII-IX locations on the MMI scale. The rapid loss estimation of CEDIM/CATDAT/Risklayer, gives a total damage value coming out to between 0.49 and 1.56 billion USD with a replacement cost (0.64 to 1.9 bn USD) in the order of 30 % of the provincial GDP (although damage does occur from outside Elazig). The exposed stock with some damage to earthquakes was calculated to be $30 bn+. Indirect losses and total macroeconomic effects are expected to increase this estimate.
to the report (28 January 2020) |
2019
|
Flooding in Venice 2019 (Italy)
|
|
 |
In November 2019 Venice experienced the second largest flood since 1872. The world-famous St. Mark's Square was more than one meter high under water and also St. Mark's Cathedral badly suffered from the flood. During the autumn and winter months, flood events frequently occur in the lagoon city; however, there has never been a series of four consecutive extreme flood events within only 5 days before.
to the report (19 November 2019) |
|
Exceptional severe thunderstorms with large hailstones June 2019 (Germany)
|
|
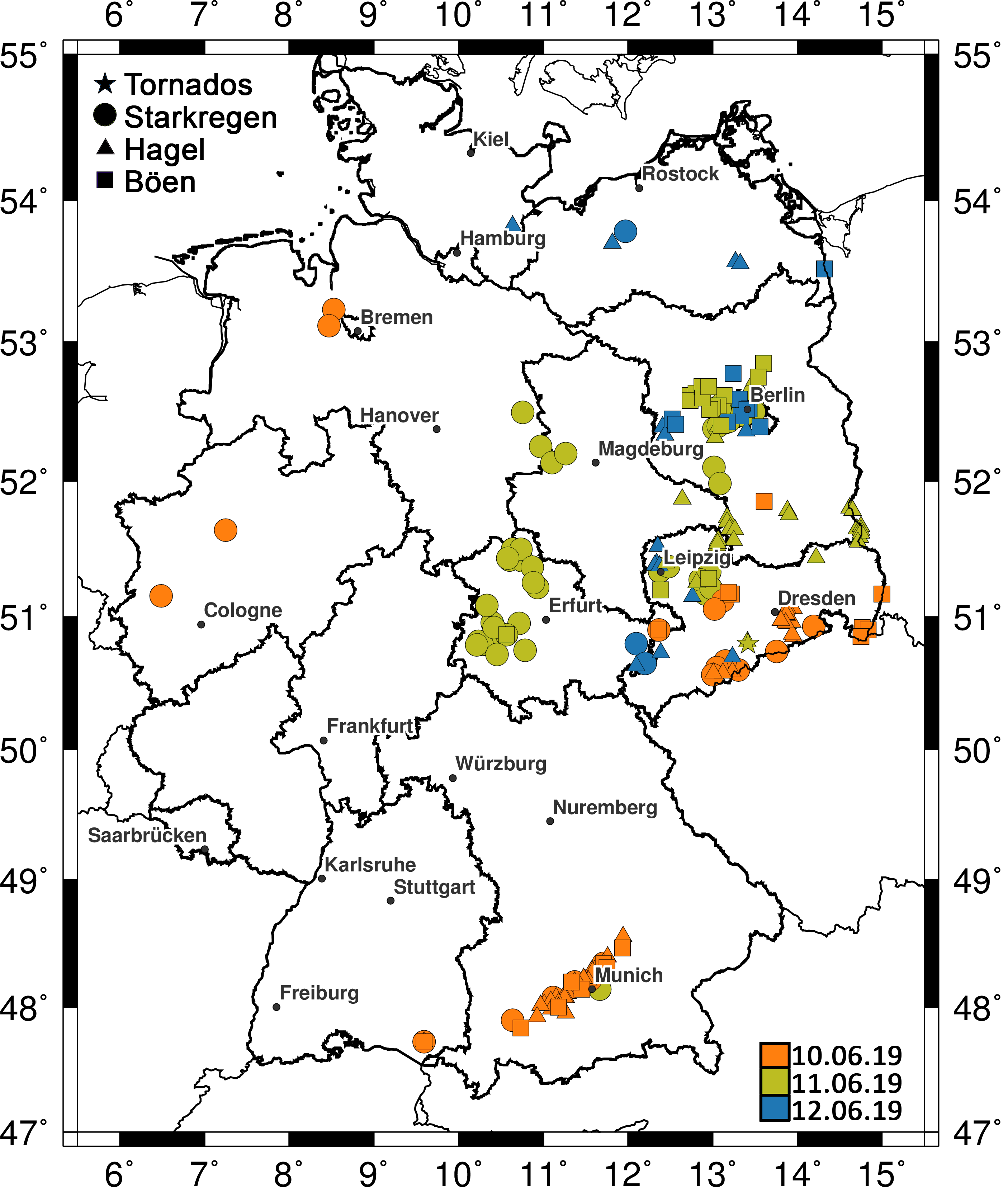 |
In the period from 10 to 12 June 2019, several severe thunderstorms associated with hail, heavy precipitation and severe wind gusts caused considerable damage to buildings, vehicles, infrastructure and agriculture in south-eastern and eastern Germany. On Pentecost Monday, 10 June, large hail with a diameter of up to 6 cm affected many suburbs of Munich and the districts of Freising, Dachau, Landsberg/Lech, Ammersee, Wörthsee and Kaufbeuren. Numerous trees fell by gusts up to 120 km/h, railway traffic was severely restricted, and delays and flight cancellations also occurred at Munich Airport. Over the next two days, numerous thunderstorms developed, especially in eastern Germany, some of which were accompanied by heavy rain and hail. Among other things, these caused severe disruptions in the metropolitan area of Berlin. On June 11, the Berlin-Buch station reported a total rainfall of 46.2 mm in one hour, with Ueckermünde in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania reporting heavy gusts of up to 89 km/h a little further northeast. On 12 June, a tornado was observed in Tauscha, Saxony, some 20 km north of Dresden, which caused considerable damage to 30 to 40 houses. The Gesamtverband der Deutschen Versicherungswirtschaft (GDV) estimated the loss amount for the three days one week after the event at 650 million euros. Although the losses did not reach the magnitude of the famous Munich hailstorm in 1984 or the storm episode in July 2013 with severe hail damage at Reutlingen and Wolfsburg, the event is still one of the ten hailstorms with the highest losses in the last 20 years.
to the report (14 July 2019) Wilhelm, J., Mohr, S., Punge, H. J., Mühr, B., Schmidberger, M., Daniell, J. E., Bedka, K. M., Kunz, M. (2021): Severe thunderstorms with large hail across Germany in June 2019. Weather, 76, 228–237, doi:10.1002/wea.3886. |
|
Heavy Rain (Germany)
|
|
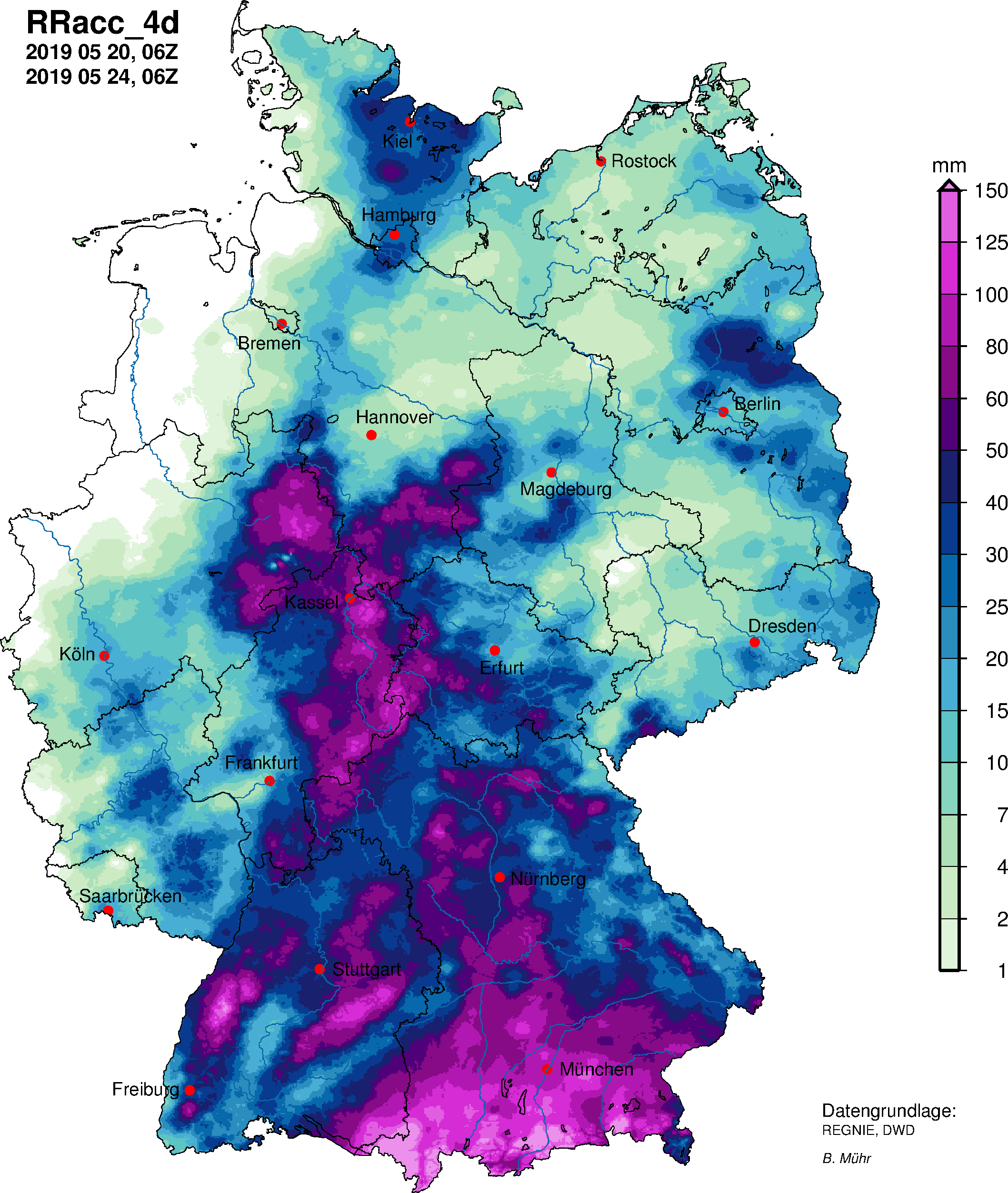 |
Rainfall lasting more than two days, which occasionally reached more than 200 mm, especially in the center and south of Germany, led to rapidly swelling streams and rivers. Many of them were flooded and in East Hesse two levels of Fulda tributaries even reached new historic highs. On many rivers in Hesse, Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria, floods occurred with a return period of between 2 and 10 years. However, there was no extreme flood on larger rivers. In some areas streams and rivers came out or overflowed their banks and flooded adjacent properties, meadows and roads. Some road connections were interrupted and the railway between Murnau and Garmisch was also closed. The heavy rainfall was caused by a low-pressure system with a center above eastern Central Europe; on the one hand, it transported moist and warm air masses in a wide curve from north to Germany, and on the other hand, the strong northern flow brought an effective moisture replenishment, which was particularly noticeable in the low mountain ranges and close to the Alps increasing precipitation. The large rain deficit that has existed in Germany for many months was able to reduce, but not to eliminate it. In addition, rainfall was particularly low in the particularly dry regions in the north-east of the country.
to the report (25 May 2019) |
2018
|
Volcano-Tsunami Anak Krakatoa
|
|
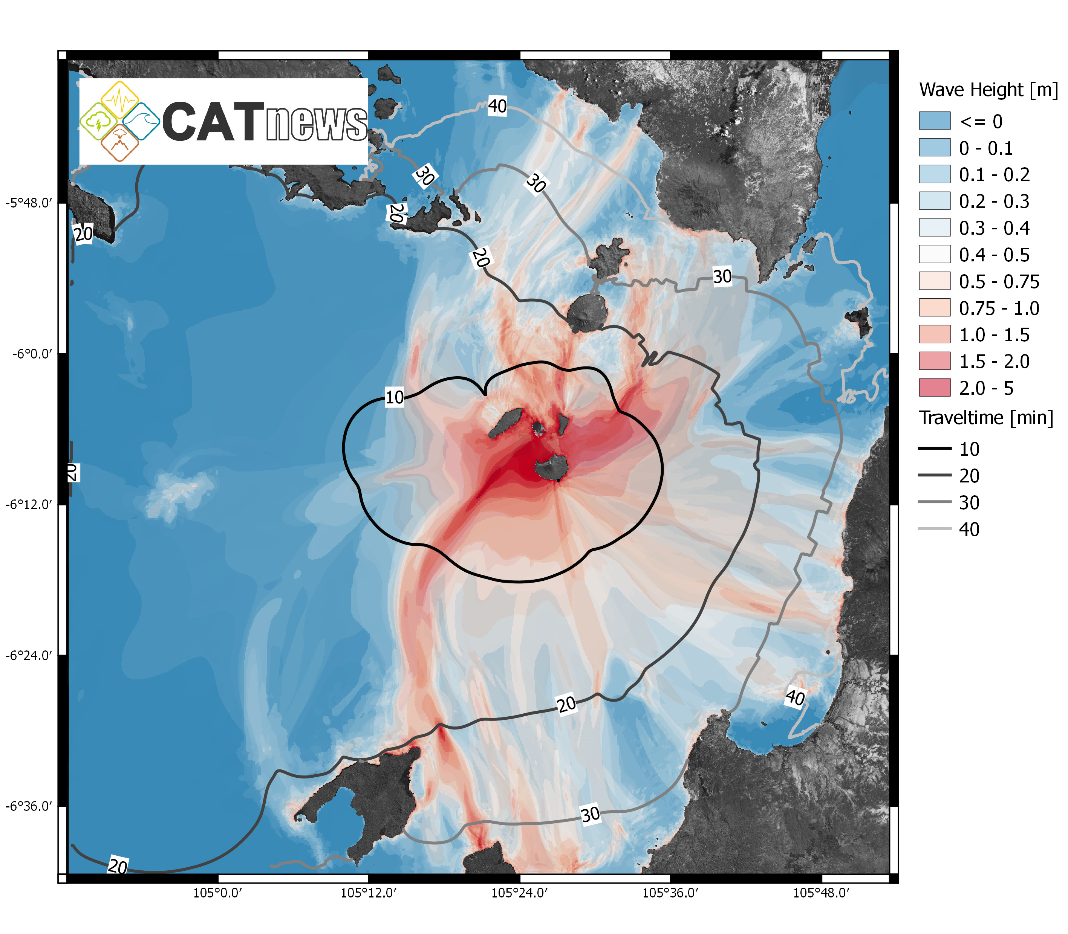 |
The vulcano Anak Krakatoa is the successor volcano of the great Krakatoa which erupted in 1883. The volcano is known for its significant growth during the last decades. On Dec. 22nd, 2018, after a probable eruption of the volcano, parts of its South-Western flank slid into the ocean including an unknown underwater volume. This landslide triggered a tsunami which affected almost all coasts in the Sunda Strait within 30-50 min. Since the local time was in the early evening, the tsunami waves arrived at the coasts without great visual clues such as receding water leaving the people unprepared. In the province of Indonesia 'Lampung', the tsunami wave coincided with a high tide leading to an amplification. The wave pattern led to very local major inundations of up to 6m and 1-3m in a wider area. Quickly after the flank collapse, the volcano continued with major eruptive activity for several weeks including various stronger exposions, leading to a significant loss of mass, reducing its height by about 220 m.
to the report (2 April 2019) |
|
Hurricane Florence (USA)
|
|
 |
With FLORENCE, the sixth tropical system of the Atlantic hurricane season 2018 was named and became the third hurricane of the season and the first major hurricane of at least category 3 in 2018. FLORENCE was an unusally long-living storm and become a category 4 hurricane on 5 September 2018 and once again on 10 September 2018. Inbetween there was rapid weakening and re-intensification of the tropical system. The highest average wind speeds were 225 kph, gusts reached 269 kph, the lowest air pressure in the center was 939 hPa.
to the report (26 September 2018) |
|
Earthquake Lombok (Indonesia)
|
|
 |
The Lombok earthquake of August 2018 was a shallow earthquake with a magnitude of 6.9 Mw that struck the Indonesian island of Lombok on the morning of August 5, 2018. Much public and critical infrastructure damage occurred, and in addition there was damage to tourist facilities in various locations across Lombok especially on the western coast. It is still expected that the damage will be insignificant for the insurance industry.
to the report (7 August 2018) |
|
Storm Friederike (Western and Central Europe)
|
|
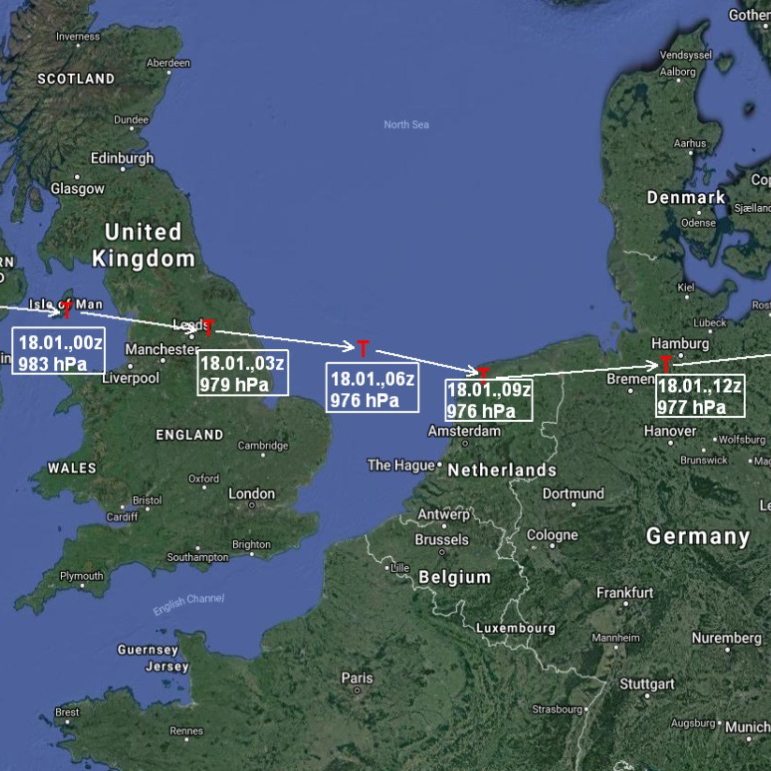 |
On 18th January 2018, on the same day of the week and date as Orkan "Kyrill" in 2007, hurricane "Friederike" swept over a broad strip of Benelux across Germany to Poland. The gusts reached hurricane strength down to the lowlands (138 km/h in Gera), on the Brocken in the Harz was 204 km/h and the nationwide record gusts during "Kyrill" (202 km/h, Wendelstein) was exceeded.
to the report (31 January 2018) |
2017
|
Excessive Indian Monsoon
|
|
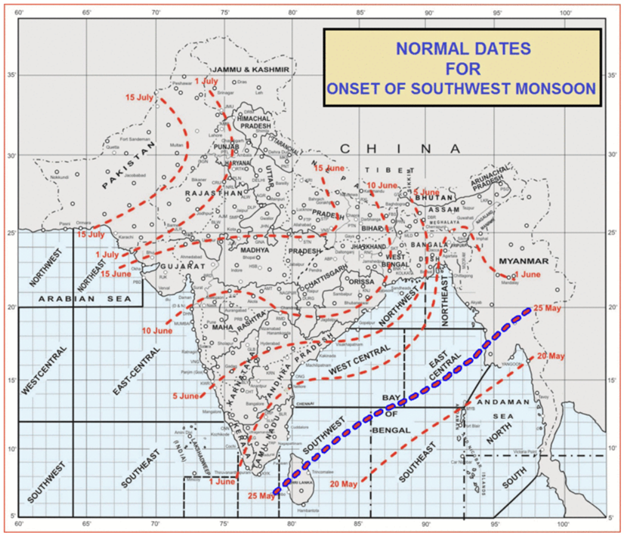 |
Localized excessive rain amounts related to 2017 Indian summer monsoon led to devastating flooding in some parts of northern and north eastern India as well as in parts of Nepal and Bangla Desh. The death toll rose to more than 2000 people. Torrential rain made buildings collapsing and left part of cities underwater. Furthermore, vast areas of land were flooded in the state of Uttar Pradesh, thousands of villages were submerged and flooding affected millions of people. However, overall averaged rain amounts for India didn’t show unusual values. Also the timing of the onset of the monsoon was pretty much what has to expected on average.
to the report (6 September 2017) |
|
Winterstorm 'Egon', Western and Central Europe
|
|
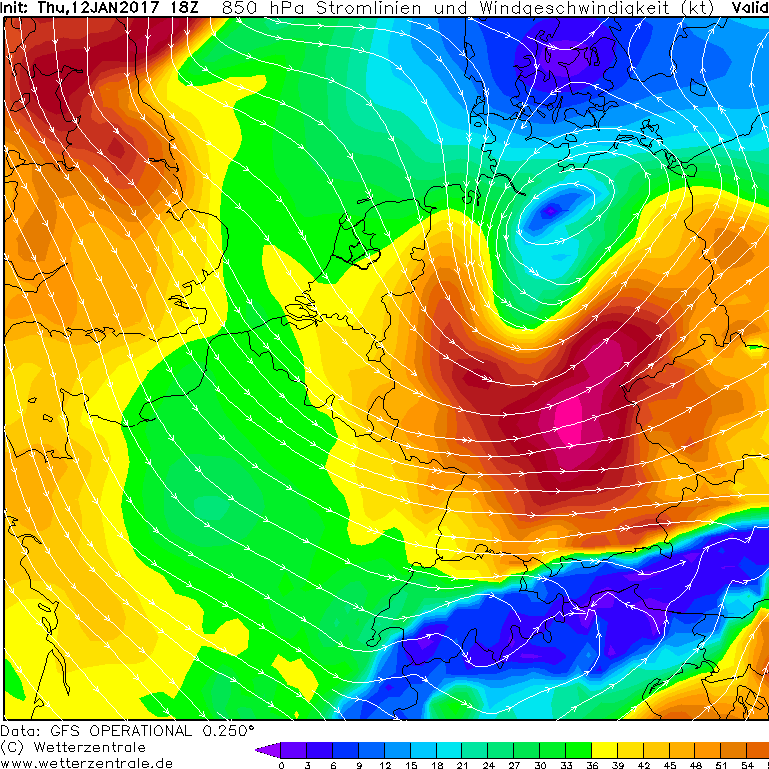 |
A strong frontal zone developed above the Atlantic Ocean at the 10th and 11th of January 2017. The resulting ground depression "Egon" moved, while strenghtening, from Brittany across Belgium to Lower Saxony in the morning of the 13th of January. The weather station on the Weinbiet in Rhineland-Palatinate measured a gust with 148 km/h. Besides strong wind, heavy snowfall on the northern part of the depression caused substantial traffic obstruction resulting in numerous accidents in the southern and central part of Germany. Storm and Snow caused damage to buildings, power lines and parking cars.
to the report (17 January 2017) |
2016
|
Amatrice Earthquake, Central Italy
|
|
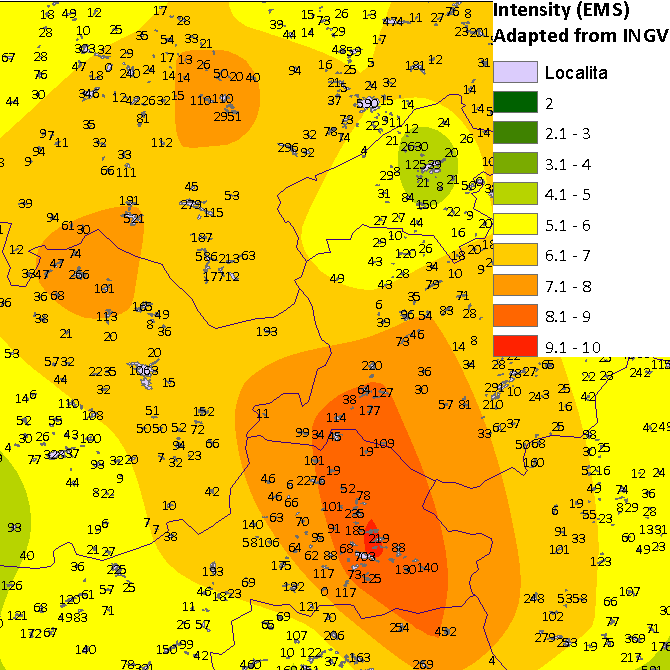 |
On the 24th of August in 2016 an earthquake hit the regions Rieti and Ascoli Piceno in Italy at 01:36:32 UTC. The most impact was in Amatrice, Accumoli and Pescara & Arquata del Tronto. The Epicenter was located at 42.704 latitude and 13.238 longitude. The Hypocenter was located at 4.2 km depth. The magnitude 6.0 (Mw) earthquake lasted for 15 seconds. The sad results of the disaster are 268 death, 400 severe injured, 4000+ sheltered homeless.
to the report (26 August 2016) |
2015
|
Extreme Rain Event, Central Europe
|
|
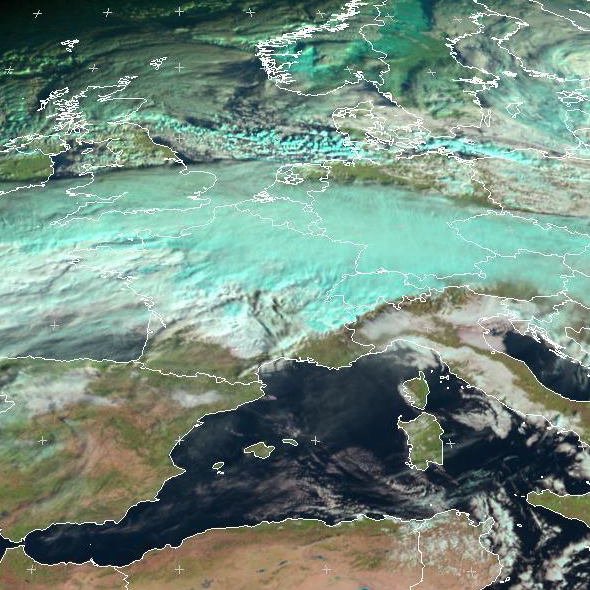 |
An extreme rain event in Central Europe from the 19th to the 21st of November in 2015 was caused by the low pressure systems "Iwan", "Kunibert" and "Jürgen". 150-200 mm of water fell within the 36 to 48-hour event (start around 11 UTC), which is extraordinary. Considering the 24 period (00 to 00 UTC), the Feldberg rain amount was a new record. Nevertheless, the enormous high rain amounts had only minor impacts because nearly all rivers in Bavaria, Baden - Württemberg and Switzerland were at low water before the rain event.
to the report (23 November 2015) |
|
Greece Earthquake
|
|
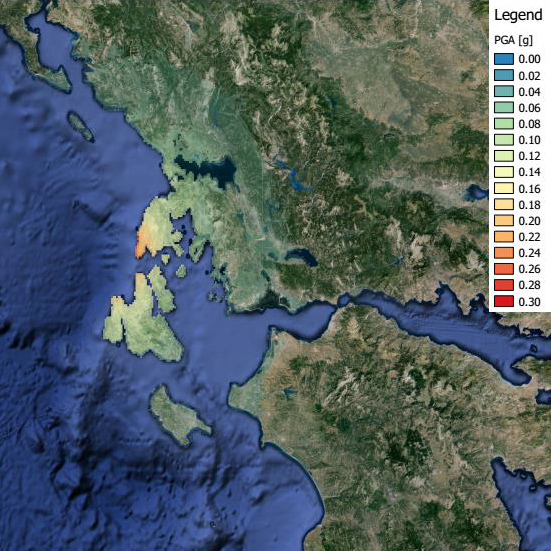 |
On the 17th of November in 2015 an earthquake hit the island Levkas in Greece at 07:10:09.1 UTC. The Epicenter was located at 38.66 latitude and 20.6 longitude. The Hypocenter was located at 10 km depth. The magnitude 6.4 (Mw) earthquake lasted for 50 seconds. In southern Lefkas Island, there have been 20 uninhabitable, 120 houses damaged, with one death coming from a collapsed stable. On Ithaka, 40 houses were damaged and on Kefalonia there were also reports of building damages.
to the report (23 November 2015) |
|
Chile Earthquake
|
|
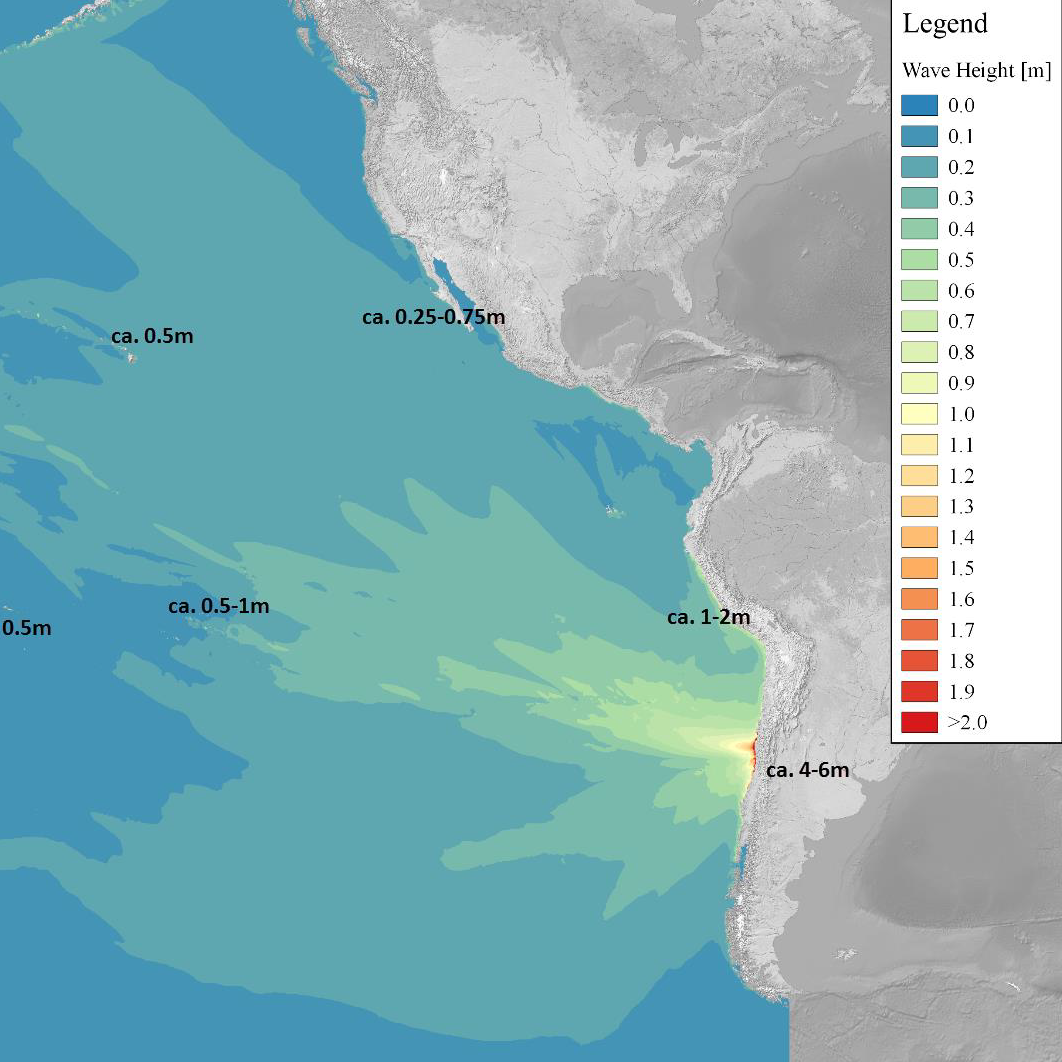 |
On the 16th of September in 2015 an earthquake hit the regions Coquimbo and Valparaiso in Chile at 22:54:33 UTC. The Epicenter was located at -31.57 latitude and -71.65 longitude. The Hypocenter was located at a depth of 25 km. The magnitude 8.3 (Mw) earthquake lasted for 80 seconds. Based on news reports, there had been minor damage to buildings in various locations, landslides and tsunami inundation damage close to the epicenter.
to the report (19 September 2015) |
2013
|
Winterstorm 'Xaver', Germany/Denmark/Great Britain
|
|
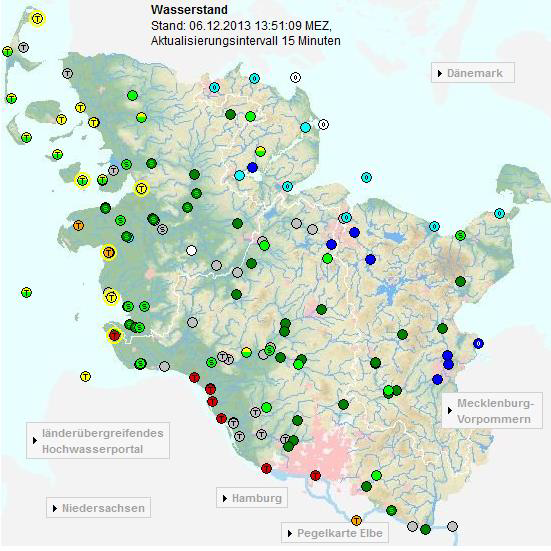 |
Storm “Xaver” developed on 4th of December in 2013 in a zone of high horizontal temperature contrast between Newfoundland and Greenland. During continuous intensification, the storm moved further over Scotland to Southern Sweden on 5th -6th of December
to the report (6 December 2013) |
|
Philippines (Bohol) Earthquake
|
|
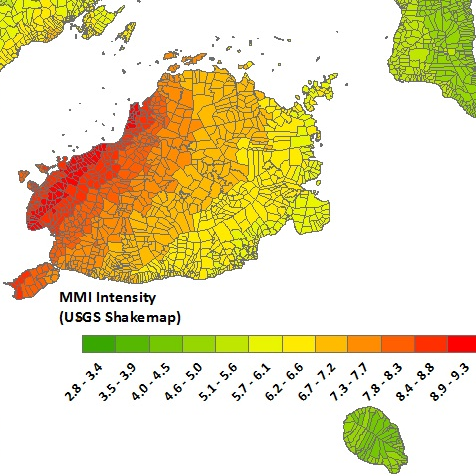 |
On the 15th of October in 2013 an Earthquake hit the islands Bohol and Cebu in the Philippines at 12:12:31 UTC. The Epicenter was located at 9.86 latitude and 124.07 longitude. The Hypocenter was located at a depth of 12 km. The magnitude 7.2 (Mw) earthquake lasted for 30 seconds. The counting of buildings destroyed has not been undertaken with only a few houses included in the current count of 10020 destroyed and 35621 damaged. Based on families displaced, this value could be up to at least 15000 destroyed.
Bericht 6 (02 November 2013)
|
2012
|
Typhoon 'Saola', Philippines and Taiwan
|
|
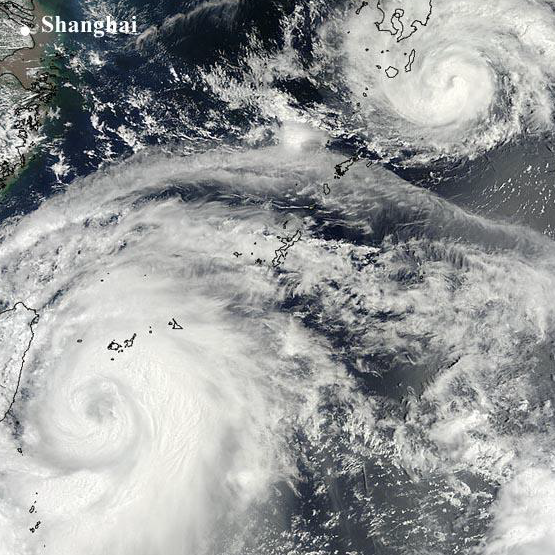 |
Extensive flooding, landslides, more than 30 fatalities, many injuries, thousands of homeless people- this is the result (first estimation) of the tropical cyclone (TC) Saola that crossed first over the Philippines and afterwards over Taiwan in the period from 28th July to 3rd August 2012. TC Saola moved very slowly over Taiwan, leading to extreme precipitation totals in excess of 1000 mm in 48 h at some stations. The track of Saola including the huge precipitation totals were not properly predicted by the weather forecast models.
to the report (3 August 2021) |

